LCF Assessment of GT Exhaust Welded Joints Using Calibrated Transient Thermal Analysis
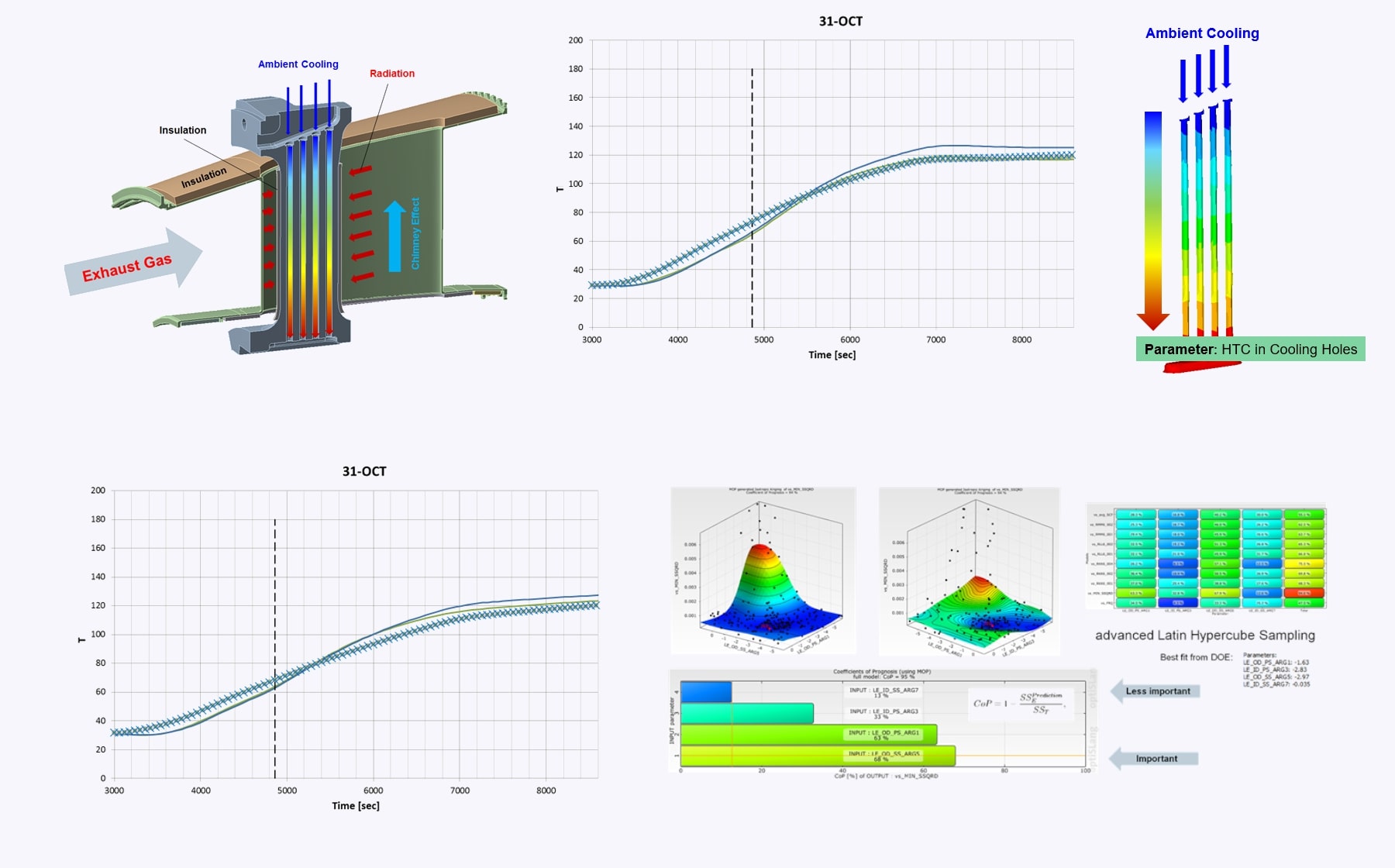
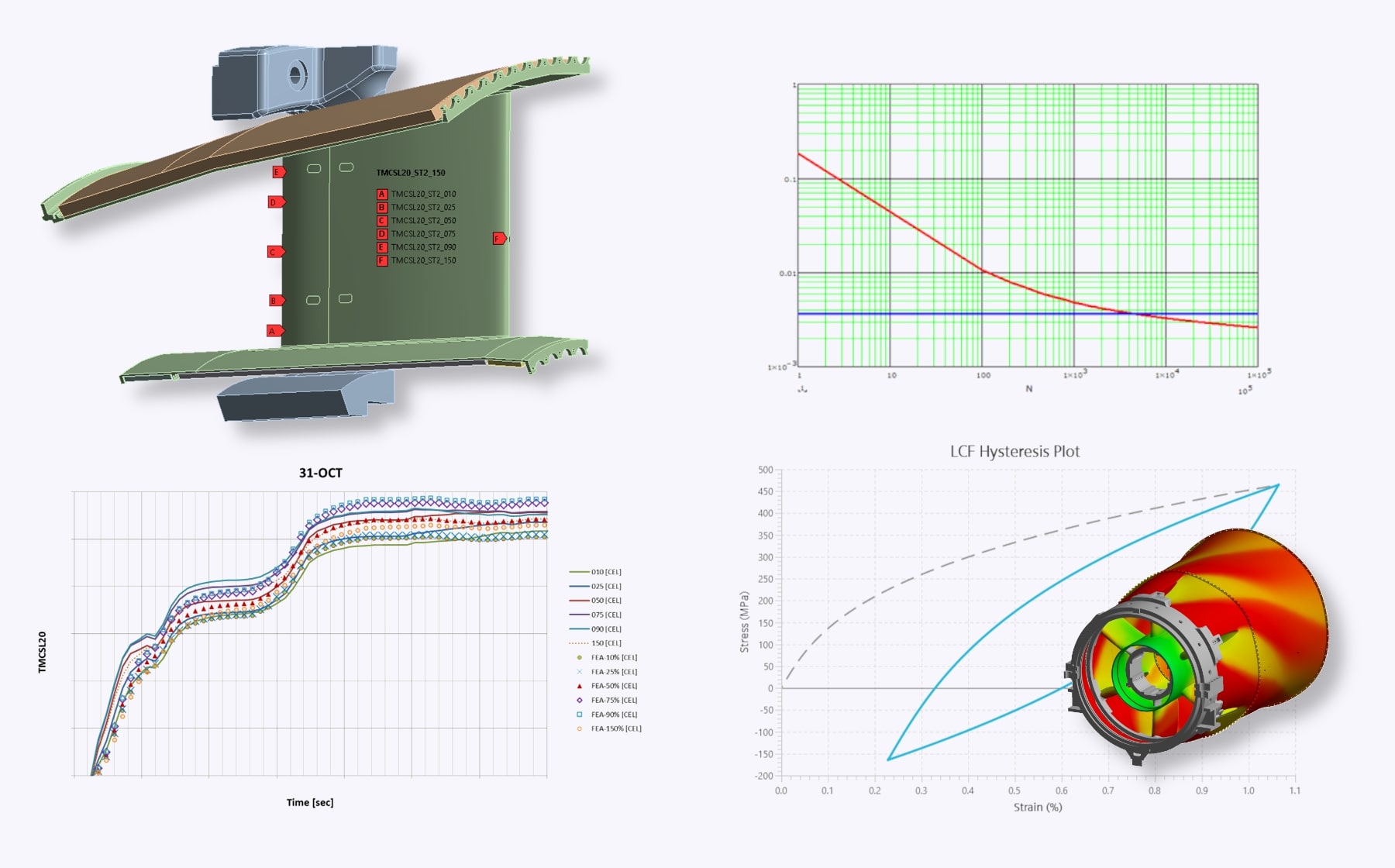
The project aimed to assess the fatigue behavior of exhaust welded joints and investigate the root cause of cracking observed during inspections. A 1D thermal-fluid simulation model was developed and calibrated using operational measurements (metal and fluid temperatures, flow rates, speed). Parametric optimization with optiSLang identified key parameters such as cooling HTC and thermal contact conductance. The validated model was used to estimate service life and perform improved LCF evaluations.
- Post-processing of measurement data (fluid and metal temperatures, mass flow, power, speed, etc.)
- Creation of a parametric model including 1D fluid network, radiation, insulation, and measured inputs
- Definition of probe locations aligned with thermocouple test points
- Definition of key parameters (cooling air HTC, thermal contact conductance,…)
- Design of Experiments (DoE), meta-model creation, and optimization using Latin Hypercube sampling
- Identification of optimal parameters and validation via simulation
- Comparison of results with measurement data (transient temperature deviation < 10 K over the relevant time period)
- LCF analysis using calibrated boundary conditions
- Tools used: optiSLang, Ansys