Thermal-Structural Root Cause Analysis of Cracking in Hot Blast Valve Center Plate
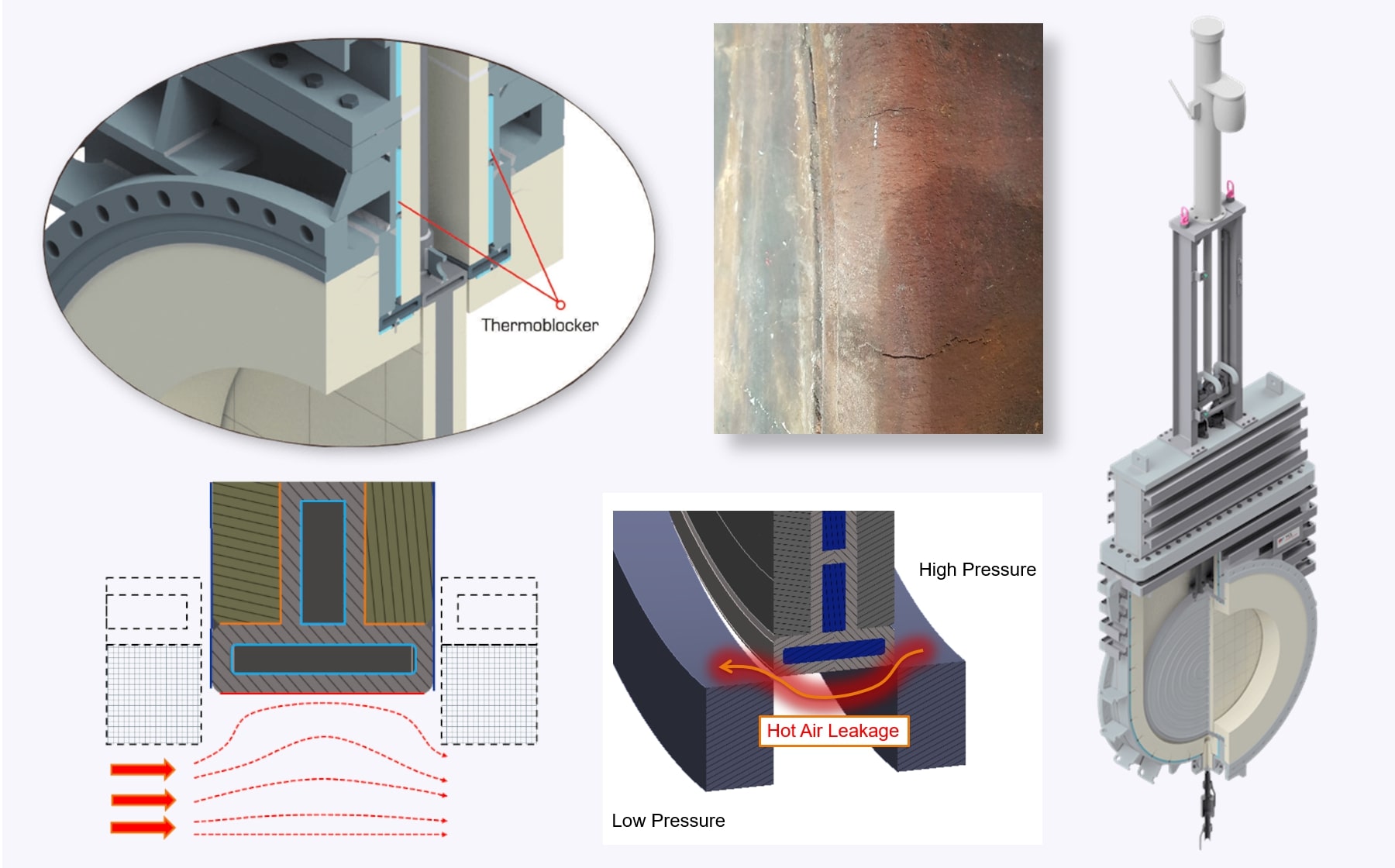
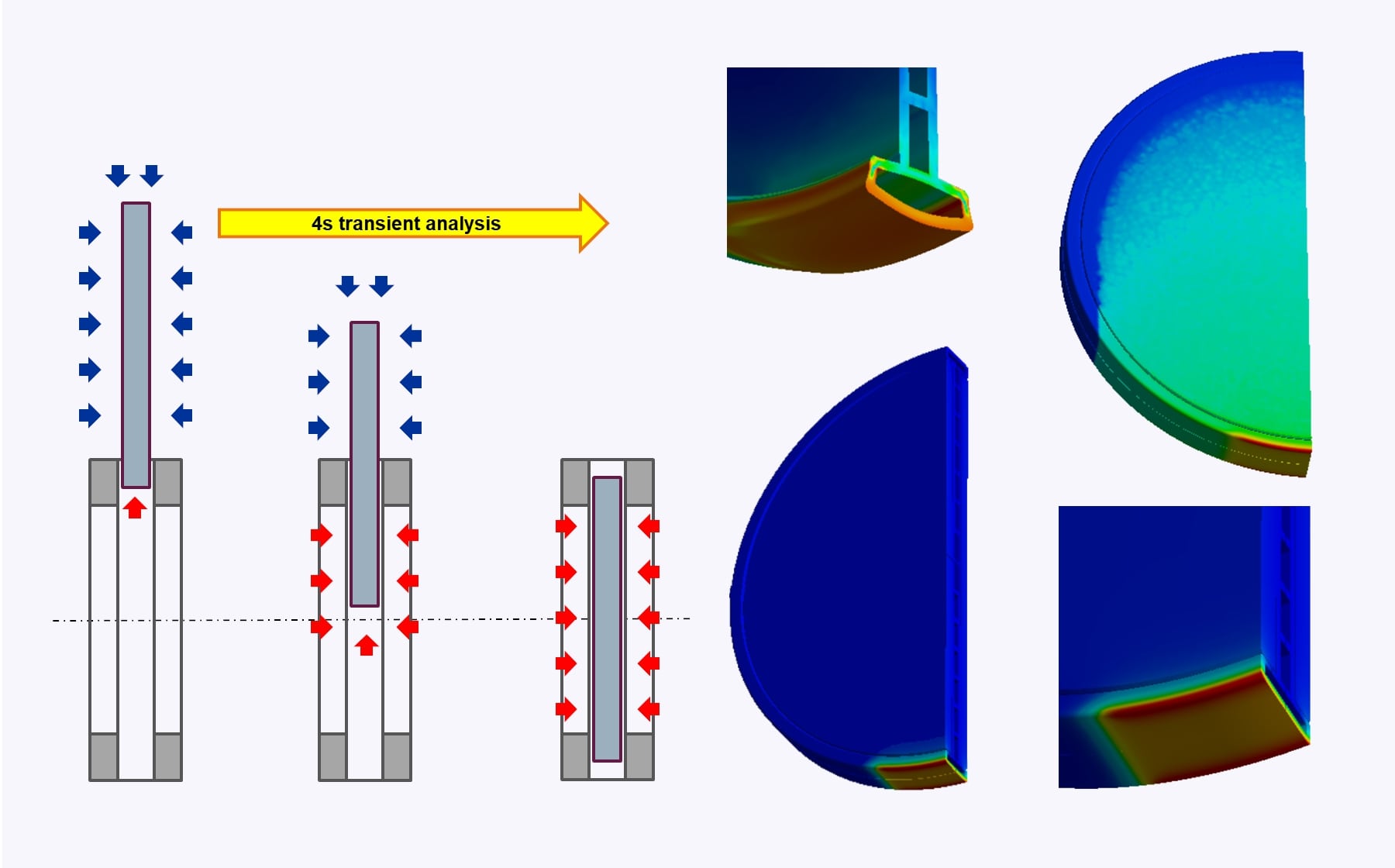
A root cause analysis was conducted to investigate cracking at the center plate of a hot blast valve. The study included several steady-state and transient thermal-structural simulations to evaluate possible damage mechanisms such as overheating and cooling failure due to internal deposit buildup. The valve design involves a vertically moving, water-cooled plate actuator operating under extreme temperatures (up to 1500 °C) and pressures. Observations suggested that local overheating and limited cooling effectiveness may have contributed to premature material failure.
- Steady-state and transient thermal-structural analyses of the hot blast valve center plate
- Assessment of the effect of depositions in the ring cooling channel on heat transfer performance
- Parametric study of HTC reduction due to deposition thickness and its impact on local temperature
- Consideration of alternative scenarios (e.g. pressure-driven gas leakage, incomplete closure)
- LCF life estimation to quantify life sensitivity to deposition buildup