Reduction of Flow Separation at the Exit Duct of a Hot Blast Stove Using CFD Simulation
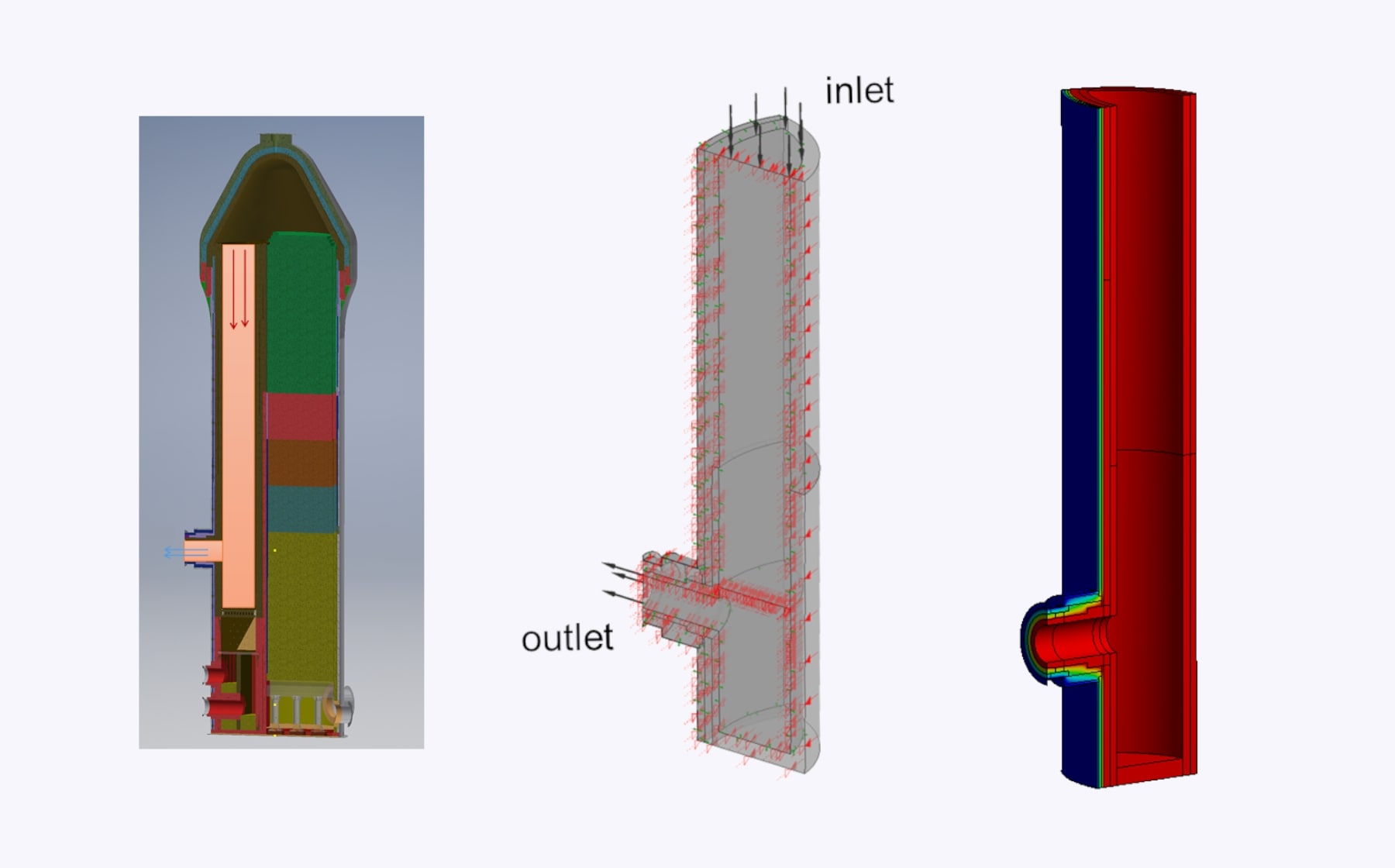
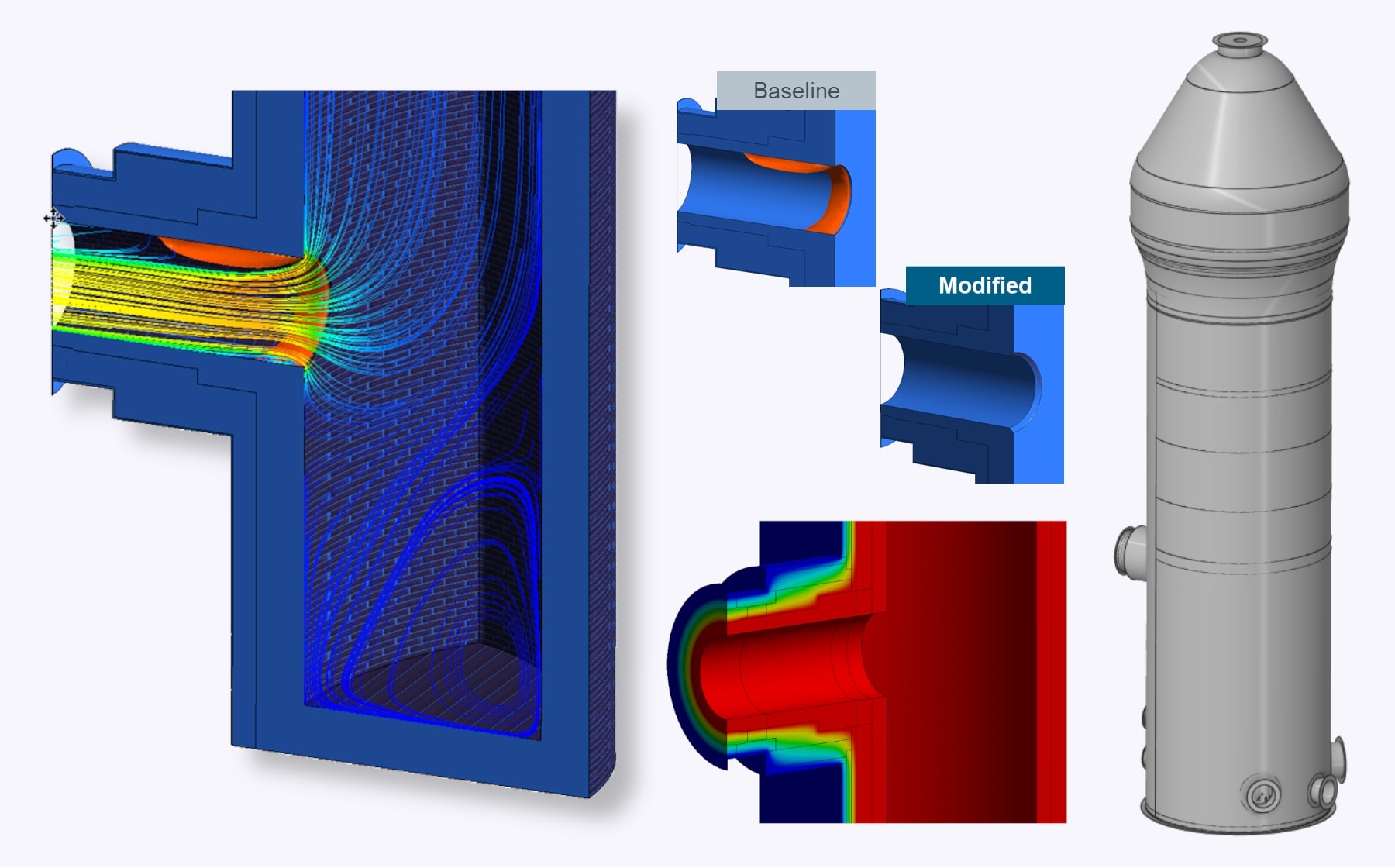
A combined steady-state and transient CFD simulation with conjugate heat transfer was performed to evaluate the exit duct of a hot blast stove. Two design variants were investigated: the baseline and a modified version featuring an optimized chamfer at the duct edge. The baseline design showed significant flow separation at the sharp edge, resulting in shear stress and pressure pulsations on the duct wall—potential causes of local fatigue or erosion. The chamfered design effectively suppressed flow separation, with separation bubbles nearly eliminated. Thermal effects from the modification were found to be local and insignificant.
- Combined steady-state and transient CFD simulation with conjugate heat transfer
- Evaluation of the exit duct in a hot blast stove
- Comparison of baseline and chamfer-optimized duct edge design
- Flow separation analysis and wall shear stress evaluation
- Assessment of pressure pulsations as potential fatigue or erosion drivers
- Evaluation of local thermal effects due to geometry modification