
Manufacturing Support
Engineering analyses support manufacturing processes — from additive manufacturing and welding to assembly validation. Thermal, structural, and flow simulations are used to assess feasibility, process stability, and dimensional accuracy. Additive processes are evaluated for thermal gradients, distortion, and residual stresses. Welding simulations help predict heat-affected zones, residual stresses, and joint integrity. Assembly checks include virtual evaluations of tolerances and geometric deviations — enabling optimized fixture design, process planning, and quality assurance.

Key Capabilities
- Simulation-based support for additive manufacturing — including powder bed fusion and directed energy deposition (DED)
- Welding analysis — prediction of heat-affected zones, residual stresses, and thermal cycles
- Virtual assembly validation — assessment of geometric deviations and tolerance stacks
- Transient thermal and mechanical modeling of manufacturing processes
- Evaluation of manufacturing and quality deviations — including casting deviations, machining errors, assembly misalignments
More information
Additive Manufacturing Simulation
Supports powder bed fusion and directed energy deposition (DED) processes through transient thermal and mechanical analysis. Simulations predict temperature distribution, solidification patterns, distortion, and residual stresses during build-up. These results enable optimization of printing strategies, support configuration, and post-processing requirements.
Example: Thermal and stress analysis of a diffuser built using DED — assessing distortion and residual stress accumulation during multi-layer deposition.
Welding Analysis
Evaluates weld performance by simulating heat input, cooling rates, and thermal cycles. Heat-affected zones (HAZ), residual stress fields, and potential distortion are predicted based on weld path, material behavior, and fixture constraints.
Example: Residual stress prediction in an exhaust liner weld — supporting future assessment of fatigue strength.
Assembly Support
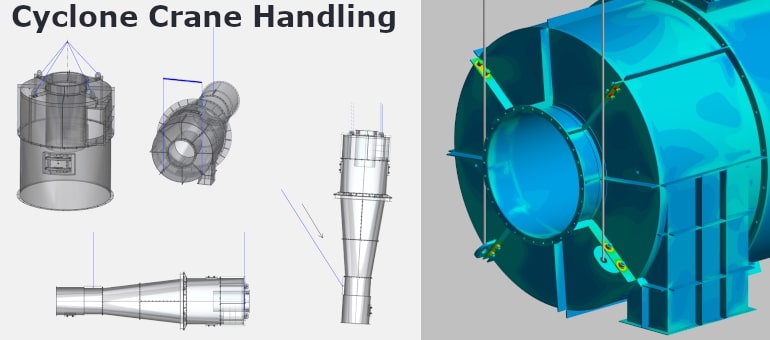
Supports critical steps of component assembly through structural and functional assessments — including handling operations such as crane lifting, slinging, and transportation under mechanical loads. Evaluations may consider cold ambient conditions, which could potentially require design or procedural modifications.
Example: Structural analysis of a separation cyclone during crane handling at sub-zero temperatures — including assessment of slinging points and lifting stability.
Evaluation of manufacturing and quality deviations
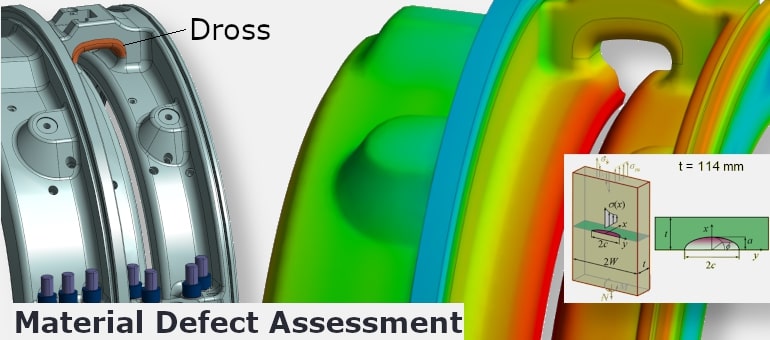
Assesses the structural and functional impact of deviations arising from manufacturing processes — including casting, machining, and assembly. Simulations account for geometric imperfections, misplaced features, local defects, and material property changes.
Example: Assessment of a dross region in a cast component — evaluating its effect on local stress concentration and fatigue strength under cyclic loading.
Process Simulation
Captures transient thermal and mechanical behavior during manufacturing — such as heating, cooling, or forming processes. These analyses help evaluate process timing, material response, residual stresses, and fatigue potential.
Examples: Simulation of thermal assembly process — or quasi-static forming simulation to assess strain distribution and springback effects.
