
Structural Analyses
Structural integrity and reliability are ensured through detailed assessments under static, dynamic, and thermal loading conditions. Advanced simulation techniques — including linear and nonlinear finite element analysis, buckling evaluations, vibration studies, and fatigue assessments — are applied to verify the performance of complex components.
Applicable across all industries and component types, from pressure vessels and support structures to bolted/welded joints and rotating machinery.

Key Capabilities
- Strength and thermal-stress evaluation — proof of functionality
- Buckling, vibration, and response analyses
- Nonlinear dynamic simulations
- Fatigue and lifetime predictions
- Code-compliant verification
- Design support and simulation-based optimization
More information
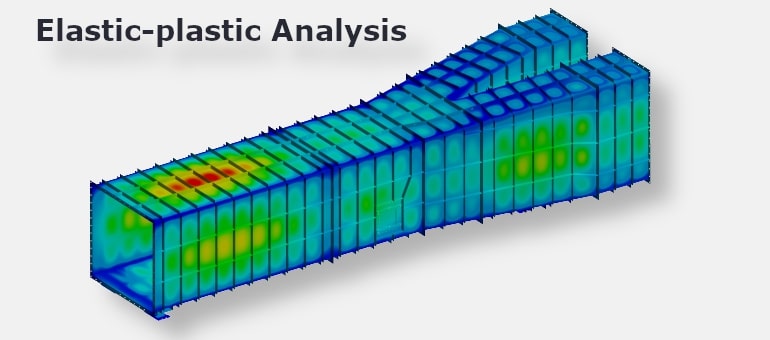
Non-linear Static incl. Creep&Plasticity
Evaluates structural behavior beyond the elastic range, including permanent deformations, plastic yielding, and time-dependent creep effects under constant load and temperature.
Example: Creep deformation in a high-temperature turbine casing under sustained vane loads.
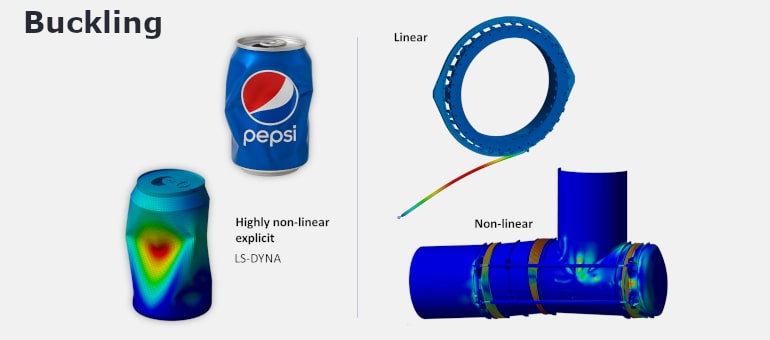
Buckling
Evaluates structural stability under compressive or thermally induced stresses to identify risks of sudden collapse or loss of stiffness due to instability.
Examples: Buckling of a thin-walled channel component under vacuum load, or failure of a multi-ply expansion joint due to thermal gradient.
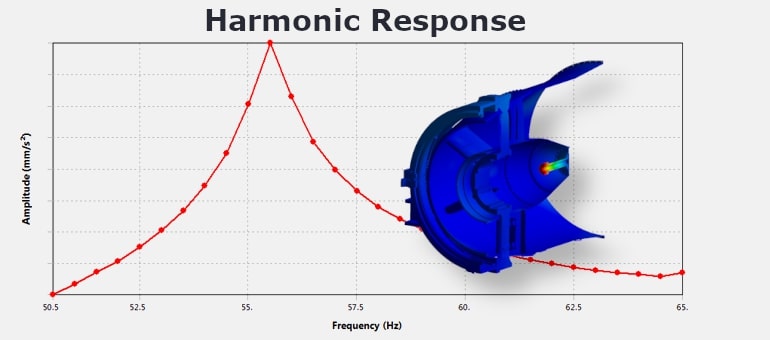
Modal & Harmonic Response
Identifies natural frequencies and mode shapes (modal analysis), and evaluates steady-state structural response to sinusoidal loading (harmonic analysis).
Example: Resonance assessment of a turbine exhaust casing excited by rotating mass imbalance.
Transient Dynamic & LS-Dyna explicit
Captures time-dependent dynamic responses under short-duration, high-intensity loads or highly non-linear deformation using explicit solvers such as LS-Dyna. Suitable for impact, crash, and large-deformation events involving multiple contact interactions.
Examples: Drop impact simulation of a battery housing under high-speed loading, or blade loss simulation resulting in damage to a turbine bearing compartment.
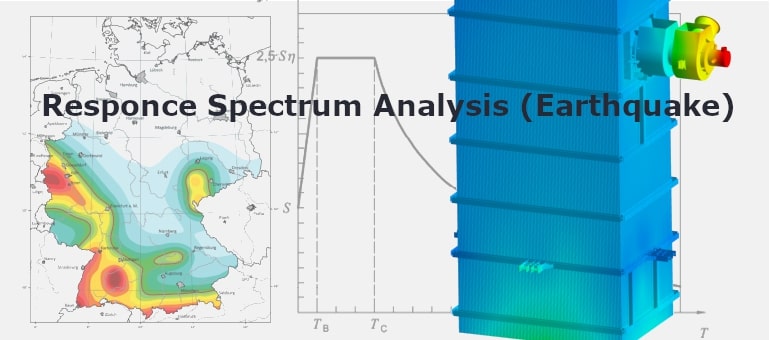
Response Spectrum
Used in seismic or shock analysis to estimate maximum structural response based on acceleration spectra rather than full time history.
Example: Earthquake safety assessment of a pressure vessel support structure per Eurocode 8.
Multi-Body Simulation (MBS)
Assemblies of rigid or flexible bodies connected by joints, constraints, and contacts to analyze kinematic and dynamic system behavior under realistic operating conditions.
Example: Motion analysis of a turbine guide vane actuation system including linkage dynamics and actuator loading.
Fluid-Solid Interaction (FSI)
Couples fluid dynamics and structural deformation to assess pressure-induced or thermally driven loading and the resulting structural response in real-time. Especially relevant where fluid forces and structural deflection interact dynamically.
Examples:
- Forced Response Analysis: Structural stress evaluation of a diverter damper blade under time-varying aerodynamic loads from unsteady CFD. Pressure fields are mapped — after FFT processing — to the structure to assess vibratory stresses and fatigue risk.
- Quasi-Static Stress Evaluation: Strength verification of a damper blade under peak pressure distribution extracted from steady-state CFD during full-load operation. Used to assess maximum stress and deformation without accounting for time-dependent effects.
